History of road development:-
1. Roman road:-
The earliest large scale road conditions is attributed to romans who contacted an extensive system of roads radiating in many directions from Rome.
Appian way which was built by romans in 312 B.C. extended over a length of about 580 km.
Features of roman road:-
- They were build straight without any gradient.
- An earthed road with a graveled surface.
- The total thickness of road section worked out as high as 750 mm to 1200 mm .
- The soft soil from top was removed till the hard stratum was reached.
 |
| Roman road |
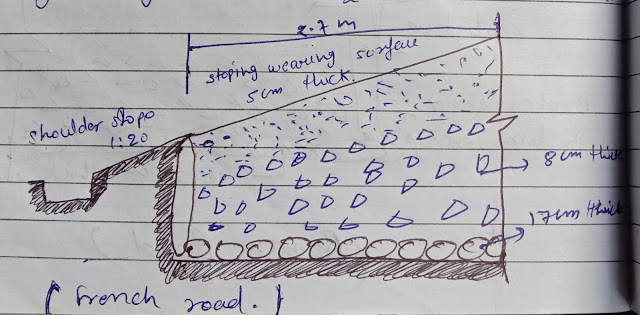
2. Tresaguest road or french road :-
- The next measure development in the road construction occured during the regime of nepolion.
- The significance construction were given by tresaguest in 1764 and a typical cross section of this road is given
- He developed a cheaper method of construction then the locally unsuccessful revival of roman practice.
- The pavement used 200 mm pieces of stone of a more compact from and shaped such that they had at least one at side which was placed on a compact formation.
- Small pieces of broken stones were they compacted into the spaces between larger stones to provide a level surface.
- Finally the running layer was made with a layer of 25 mm sized broken stones.
 |
| French road or tresaguest road |
3. Macadam road or british road :-
- The british engineer john macadam introduced what can be considered as the first scientific road construction method.
- Stone size was an important element of macadam road. 250 mm layers of well compacted broken angular stone would provide the same strength and stiffness and a better running surface than an expensive pavement founded on larger stone blocks. This he introduced an economical method of road construction.
 |
| Macadam road or British road |
4. Telford road :-
- The next development was done by scottish engineer Thomas Telford (1757- 1834).
- The foundation was prepared for a road with width of 9m and it was leveled.
- Large size stone of width equal to 40 mm and depth 170 to 220 mm were then laid .
- After filling the spaces between foundation stones ,two layer of stones having compacted thickness of 100 and 50 mm respectively laid in the center of 5.4m of width.
- The top layer of road was made of 40 mm thick binding layer of gravel.
 |
| Telford construction road |






Comments
Post a Comment